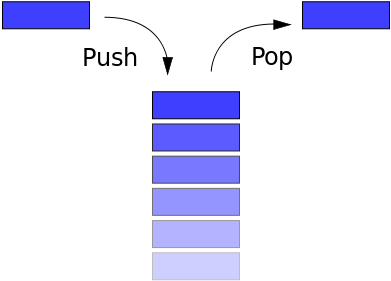
Using our implementation of a doubly linked (DL) list, we can very simply build the most basic LIFO (last in, first out) data structure: the stack.
Stacks have two basic operations: push and pop. Push pushes data onto the stack (i.e., end of the DL list) and pop pops data off the list’s tail, which is only possible because we can set the new tail as tail->prev, since we’re using a DL list, with previous pointers. Another useful function is peek, which returns a pointer to the stack’s top.
The only extra care we need here is to remind ourselves that pop only logically removes the element from the stack, so we’ll have to free the data after we’re done using it.
Here’s the code with printable tests, as usual.
/*
File: stack.c
Copyright (c) 2014 Leonardo Brito <lbrito@gmail.com>
This software is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
with this program; if not, write the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 51
Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
*/
#include "doubly_linked_list.c"
typedef d_linked_list stack;
typedef d_element elem;
stack *new_stack(int (*comparator) (void*, void*))
{
return new_list(comparator);
}
void push(stack* s, void *data)
{
add(s, data);
}
void* pop(stack* s)
{
elem* tail = s->tail;
if (tail!=NULL)
{
if (tail->prev != NULL)
{
s->tail = tail->prev;
s->tail->next = NULL;
}
else
{
s->tail = s->head;
}
}
return tail->data;
}
void* peek(stack* s)
{
return s->tail;
}
#ifdef _DEBUGGING
int main()
{
stack* s = new_stack(compare_integer);
int i, *data;
for (i=0; i<100; i++)
{
data = malloc(sizeof(int));
*data = i;
push(s, data);
}
for (i=0; i<100; i++)
{
data = (int*) pop(s);
printf("\nPopped %d",*((int*) data));
free(data);
}
return 0;
}
#endif